In the vast ocean of the internet, while most fish are friendly, there are some out to get you. They’ll try to bait you, hook you, and reel you in. This deceptive practice isn’t new. In fact, it has a name: Phishing. But what exactly is phishing, and why should you be concerned? Well, be ready as we dive deep into understanding the types of phishing attacks and how you can steer clear of these nefarious nets.
What is Phishing?
The definition of phishing revolves around a cybercrime in which attackers disguise themselves as trustworthy entities, usually via email, to extract sensitive data from victims. This could range from login credentials to financial information.
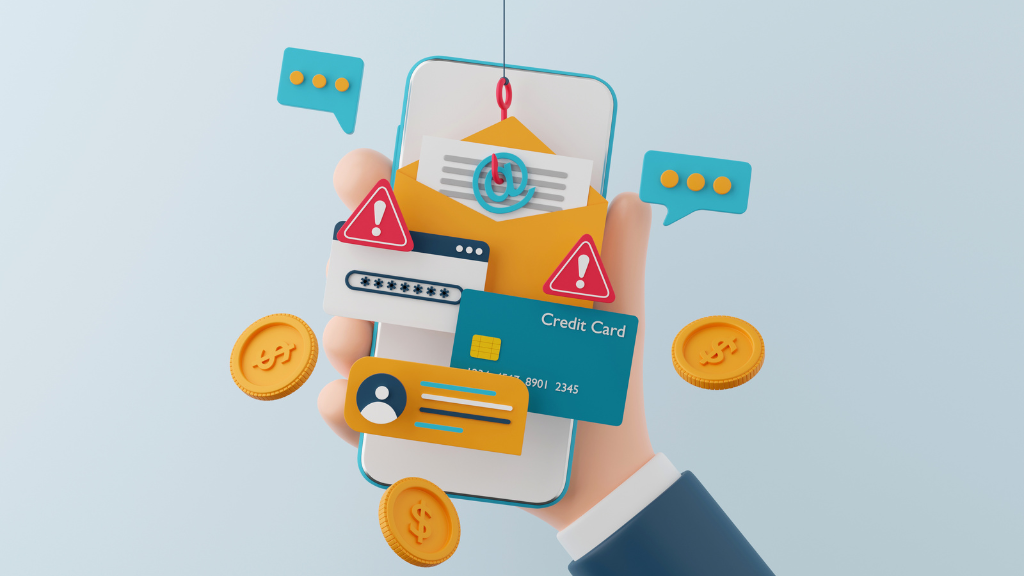

To further elaborate on the phishing definition, phishing is a technique used by cybercriminals to trick you into giving up your personal information or data by pretending to be someone or something you trust. The term itself is a play on the word “fishing,” where bait is dangled to lure the target.
At its core, phishing meaning pertains to the act of targeting individuals with deceptive messages to steal sensitive information or install malware. Now you know phishing is what type of attack. Furthermore, a variety of phishing examples abound in the digital world. For instance, this could range from deceptive ads on social media to fake login pages. Moreover, there are instances of voice phishing over the phone. media and fake login pages to even voice phishing over the phone.
Also See: How to Stop Phishing Emails in Gmail?
Types of Phishing Attacks: A Deep Dive
Email Phishing
Arguably the most well-known type of phishing, email phishing involves sending fraudulent emails to potential victims, enticing them to click on malicious links or provide personal information. Some examples of phishing emails might include a message from your “bank” urging you to verify your account details or a “colleague” sending an unexpected attachment for review.
- Classic phishing emails often come disguised as communication from trustworthy entities, like banks or service providers. These emails contain malicious links or attachments aiming to capture sensitive information.
- Spear phishing is a more targeted form of phishing. Unlike broad net phishing campaigns, spear phishing attack techniques target specific individuals or companies. Often, the attacker would have done their homework, gathering specific details to make the bait more enticing.
- Whaling is similar to spear phishing but focuses on high-profile targets, like CEOs or celebrities, aiming for a massive payout.
- Clone phishing is another type where cybercriminals replicate legitimate emails that a user has previously received, replacing the content or attachment with malicious versions.
Website Phishing
Digital miscreants often set up fake websites mimicking legitimate ones to deceive unsuspecting users.
- Fake websites trick users into entering their credentials, which are then captured by the attacker.
- Session hijacking involves stealing a user’s session token to gain unauthorized access to their accounts.
Voice Phishing (Vishing)
Vishing exploits the trust people place in voice communication.
- Fraudulent phone calls are common, where the attacker pretends to be from a bank or a similar institution and tricks the victim into providing confidential information.
- VoIP phishing takes vishing online, where attackers use internet phone services to make their deceptive calls.
SMS Phishing (Smishing)

A rising threat in the mobile age, smishing involves the use of text messages to scam individuals.
- Fake SMS alerts warn users of account issues or promise prizes, directing them to malicious links.
- Malware-laced messages trick users into downloading harmful software onto their devices.
Phishing Examples and How to Spot Them:
Just as technology advances, so do phishing techniques. Attackers continuously adapt, employing advanced tactics and more convincing disguises to lure their victims. Being aware of these evolving threats is half the battle.
- Generic Greetings: Many phishing emails start with generic greetings like “Dear Customer.” A genuine institution will likely address you by your full name.
- Suspicious Links: Before clicking on any link, hover over it. If the URL looks odd or doesn’t match the supposed sender’s website, it’s a red flag.
- Requests for Sensitive Information: Legitimate organizations will never ask for personal details, passwords, or bank information via email.
- Poor Grammar and Spelling: Many phishing emails are riddled with spelling and grammar mistakes.
- Threats or Urgent Deadlines: A common tactic is to instill fear, urging you to act quickly, often threatening account suspension or legal action.
How to Protect Yourself
- Keep software updated.
- Use two-factor authentication.
- Educate yourself and stay informed.
- Use a robust antivirus solution.
- And, of course, always think before you click.
- Seek Expert help.
Conclusion
Phishing attacks come in various shapes and sizes, each more cunning than the last. But by familiarizing ourselves with the various types and staying vigilant, we can swim safely in the vast digital ocean.
For those seeking advanced protection against these and other cyber threats, considering cybersecurity firms like Nextdoorsec can be a wise investment. With their expertise and tools, they offer an extra layer of defense against potential breaches, ensuring that you and your organization remain safe in an ever-threatening digital world.
FAQs
1. What are the 3 most common types of phishing attacks?
The three most common types of phishing attacks are email phishing, spear phishing, and smishing (SMS phishing).
2. What are the 3 steps of a phishing attack?
Preparation: The attacker chooses the target and crafts a convincing message or communication method, often mimicking a legitimate source.
Execution: The attacker sends the phishing message to the target, which could be an email, a text message, or another form of communication.
Collection: If the target takes the bait, they may provide sensitive information, click a malicious link, or download a harmful attachment, allowing the attacker to collect the desired data or gain unauthorized access.
3. What is phishing and its type?
Phishing is a cyberattack method where attackers try to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card numbers, by masquerading as a trustworthy entity. The primary types include email phishing, spear phishing, vishing, smishing, whale phishing, and pharming.
4. What are 2 types of phishing techniques?
Email Phishing: This is the most common type, where attackers send fraudulent emails designed to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information or downloading malware.
Spear Phishing: This technique involves targeted attacks against specific individuals or organizations, often using personalized information to make the attack more convincing.
5. How many attacks are phishing?
It’s difficult to specify an exact number as it constantly changes, but phishing attacks constitute a significant percentage of all cybersecurity incidents. They are a prevalent and persistent threat in the cyber landscape.
6. Which type of phishing technique involves sending text messages to a potential victim’s smartphone?
Smishing is the type of phishing technique that involves sending text messages to a potential victim’s smartphone, aiming to trick them into revealing sensitive information or clicking on malicious links.
7. What is included in a ‘Types of Phishing Attacks PDF’?
A ‘Types of Phishing Attacks PDF’ typically includes detailed descriptions of various phishing methods used in cyberattacks, such as email phishing, spear phishing, whaling, smishing (SMS phishing), and clone phishing, along with examples, prevention strategies, and how to identify such attacks.
8. What are the types of phishing attacks in cyber security?
In cyber security, common types of phishing attacks include email phishing, spear phishing (targeted attacks), whaling (targeting high-level executives), smishing (via SMS), and clone phishing (copying legitimate messages with malicious links).
9. What is spear phishing?
Spear phishing is a targeted form of phishing where attackers customize their approach to a specific individual or organization, often using personal or organizational information to make the attack more convincing.
10. What is whaling phishing?
Whaling phishing is a type of phishing attack that specifically targets high-ranking individuals within an organization, like CEOs or CFOs, often involving highly personalized and sophisticated tactics.
11. What is email phishing?
Email phishing is the most common form of phishing, where attackers send fraudulent emails designed to trick recipients into revealing personal information, clicking on malicious links, or downloading malware.
12. What is clone phishing?
Clone phishing involves creating a nearly identical replica of a legitimate email, complete with malicious links or attachments, and sending it to the victim, often claiming to be an updated or revised version of the original message.






0 Comments