In our rapidly digitizing world, businesses are more connected than ever before. This increasing connectivity, while it brings numerous benefits, also introduces a myriad of cybersecurity risks. From small enterprises to large corporations, no one is immune to the threat of a digital breach. This article delves deep into the most pressing cybersecurity threats of 2023, highlighting their risks and controls.
Cybersecurity Risks for Businesses
At the very heart of the digital age is a critical component: cybersecurity. The cybersecurity risk landscape refers to the panorama of potential vulnerabilities and threats that exist in the realm of technology and online platforms. In simpler terms, a cybersecurity risk can be understood as any potential danger associated with the loss, misuse, unauthorized access, or harm to data, systems, and reputation of an individual or organization.
One misconception that continues to linger is that only large enterprises are at risk. On the contrary, small business cybersecurity threats are very real. Limited budgets and lack of in-house security expertise make them attractive targets.
The Definitions and Categories
Clarity is crucial. When it comes to cybersecurity, risks encompass potential damages a business might face due to digital vulnerabilities.
- Cybersecurity Risk Categories: These range from technical risks like software vulnerabilities to human risks like employees clicking on a phishing email. It’s a vast spectrum, and each category has its unique set of challenges.
2. Top 10 Cybersecurity Threats of 2023
To stay ahead of cybercriminals, businesses must be aware of the evolving nature of cyber threats. Here’s a rundown of the top 10 cyber security threats this year:
1. Phishing Schemes:
Even as technology evolves, phishing remains one of the most common methods of cyberattack. Cybercriminals craft deceptive emails, messages, or websites pretending to be legitimate entities to fool users into providing sensitive data, such as login credentials or financial information. These schemes may use current events, personal details, or emotional tactics to seem more convincing.
2. Ransomware Attacks:
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts the victim’s files or locks them out of their system. The attackers then demand a ransom, usually in cryptocurrency, to restore access. The costs can range from small sums to millions of dollars, and there’s no guarantee that paying the ransom will result in the restoration of access.
3. IoT Vulnerabilities:
The Internet of Things (IoT) encompasses a variety of connected devices, from smart fridges to industrial sensors. As the number of these devices proliferates, so do the potential points of entry for hackers. Many IoT devices have weak default settings or lack regular security updates, making them attractive targets.
4. AI-Powered Attacks:
With advancements in artificial intelligence, cybercriminals are using AI to craft more sophisticated attacks. This includes predicting system behaviors, automating tasks, and designing malware that can adapt and learn to evade detection.
5. Cloud Security Breaches:

As businesses increasingly rely on cloud services to store and process data, ensuring the security of these platforms is paramount. Attackers exploit misconfigured cloud settings, weak access controls, and other vulnerabilities to access sensitive data.
6. Deepfakes & Information Manipulation:
Deepfakes use AI to create hyper-realistic but entirely fake content. This could be videos, audio recordings, or photos that appear to be genuine. They pose a significant threat as they can be used to spread misinformation, defame individuals, or even manipulate stock prices and public sentiment.
7. Supply Chain Attacks:
Instead of targeting a major organization directly, attackers may exploit vulnerabilities in its suppliers or service providers. This method has become more prevalent as it allows attackers to infiltrate high-value targets through less secure channels.
8. Zero-Day Exploits:
A zero-day exploit refers to a vulnerability in software that’s unknown to the vendor. This means there’s no patch available when the exploit becomes public. Attackers take advantage of this window of opportunity to launch attacks before a fix is released.
9. Insider Threats:
Not all threats come from external actors. Employees or other individuals with access to an organization’s systems can intentionally misuse their privileges for malicious purposes or inadvertently cause breaches due to negligence or lack of awareness.
10. Mobile Malware:
As smartphones and tablets become ubiquitous in both personal and professional settings, they are also becoming a focal point for cyberattacks. This malware can take various forms, from spyware that monitors a user’s activity to ransomware that locks out users from their own devices.
Of the numerous threats, some pose a larger threat than others. Among the biggest cybersecurity risks, ransomware remains king.
Cybersecurity Risks and Controls
Understanding the risks is just half the battle. Implementing effective cyber security risks and controls is paramount. Here are some examples:
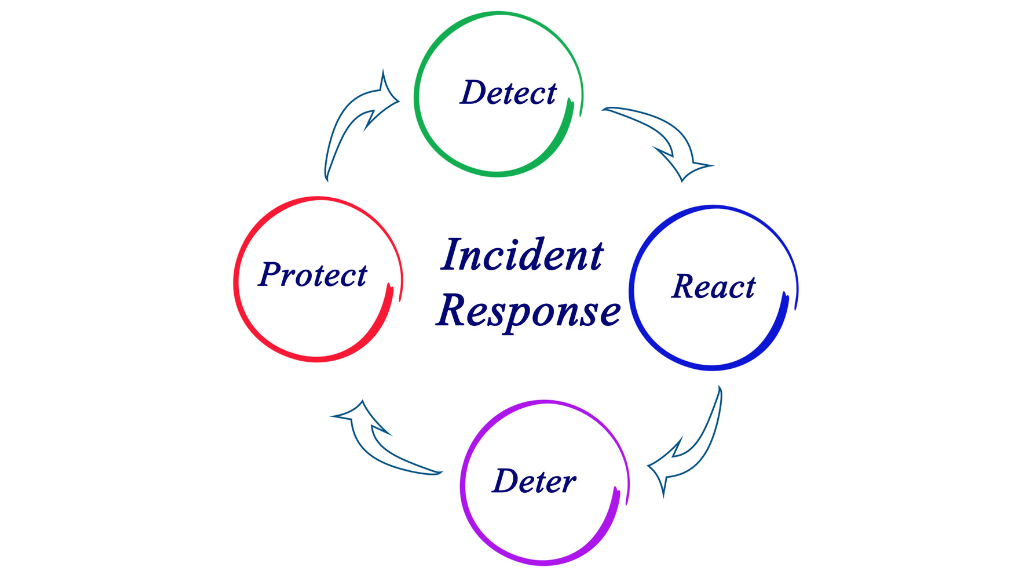
- Regular Updates & Patches: Ensure that all systems and software are up-to-date.
- Employee Training: Regularly educate staff on the importance of cybersecurity and best practices.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Always use multiple layers of authentication.
- Regular Backups: Ensure data is backed up frequently and securely.
- Incident Response Plan: Always be prepared for potential breaches with a well-structured response plan.
Conclusion
In this rapidly evolving digital age, understanding cybersecurity risks for businesses is not just essential; it’s paramount. By recognizing the threats and implementing robust controls, businesses can not only protect themselves but also thrive in this digital frontier. Remember, staying informed and being proactive are the best lines of defense.
For businesses looking to bolster their defense mechanisms, partnering with experts in the field can be the difference between remaining resilient or falling prey to a malicious attack. Firms like Nextdoorsec offer comprehensive cybersecurity solutions tailored to the unique needs of each business, ensuring that their digital assets remain secure and operations uninterrupted.
FAQs
1. What are common types of cybersecurity risks to organizations?
Organizations face risks from malware, phishing, Man-in-the-Middle attacks, DoS/DDoS attacks, password attacks, insider threats, and unpatched software.
2. What is the biggest risk in cyber security?
The biggest risk in cybersecurity is the human element, with individuals often making mistakes that lead to breaches.
3. What is the top cyber security concern your business faces today?
The top concern for many businesses today is the rise and sophistication of ransomware attacks.
4. Why should I worry about cybersecurity risks for my local business?
Because the digital realm knows no boundaries. Whether local or global, if you have a digital presence, you are a potential target.






0 Comments